IBM has created a quantum error-correcting code about 10 times more efficient than prior methods — a milestone in quantum computing research.
Today, the paper detailing those results was published as the cover story of the scientific journal Nature.
Last year, we demonstrated that quantum computers had entered the era of utility, where they are now capable of running quantum circuits better than classical computers can. Over the next few years, we expect to find speedups over classical computing and extract business value from these systems. But there are also algorithms with mathematically proven speedups over leading classical methods that require tuning quantum circuits with hundreds of millions, to billions, of gates. Expanding our quantum computing toolkit to include those algorithms requires us to find a way to compute that corrects the errors inherent to quantum systems — what we call quantum error correction.
Read how a paper from IBM and UC Berkeley shows a path toward useful quantum computing
Quantum error correction requires that we encode quantum information into more qubits than we would otherwise need. However, achieving quantum error correction in a scalable and fault-tolerant way has, to this point, been out of reach without considering scales of one million or more physical qubits. Our new result published today greatly reduces that overhead, and shows that error correction is within reach.
While quantum error correction theory dates back three decades, theoretical error correction techniques capable of running valuable quantum circuits on real hardware have been too impractical to deploy on quantum system. In our new paper, we introduce a new code, which we call the gross code, that overcomes that limitation.
This code is part of our broader strategy to bring useful quantum computing to the world.
While error correction is not a solved problem, this new code makes clear the path toward running quantum circuits with a billion gates or more on our superconducting transmon qubit hardware.
What is error correction?
Quantum information is fragile and susceptible to noise — environmental noise, noise from the control electronics, hardware imperfections, state preparation and measurement errors, and more. In order to run quantum circuits with millions to billions of gates, quantum error correction will be required.
Error correction works by building redundancy into quantum circuits. Many qubits work together to protect a piece of quantum information that a single qubit might lose to errors and noise.
On classical computers, the concept of redundancy is pretty straightforward. Classical error correction involves storing the same piece of information across multiple bits. Instead of storing a 1 as a 1 or a 0 as a 0, the computer might record 11111 or 00000. That way, if an error flips a minority of bits, the computer can treat 11001 as 1, or 10001 as 0. It’s fairly easy to build in more redundancy as needed to introduce finer error correction.
Things are more complicated on quantum computers. Quantum information cannot be copied and pasted like classical information, and the information stored in quantum bits is more complicated than classical data. And of course, qubits can decohere quickly, forgetting their stored information.
Research has shown that quantum fault tolerance is possible, and there are many error correcting schemes on the books. The most popular one is called the “surface code,” where qubits are arranged on a two-dimensional lattice and units of information are encoded into sub-units of the lattice.
But these schemes have problems.
First, they only work if the hardware’s error rates are better than some threshold determined by the specific scheme and the properties of the noise itself — and beating those thresholds can be a challenge.
Second, many of those schemes scale inefficiently — as you build larger quantum computers, the number of extra qubits needed for error correction far outpaces the number of qubits the code can store.
At practical code sizes where many errors can be corrected, the surface code uses hundreds of physical qubits per encoded qubit worth of quantum information, or more. So, while the surface code is useful for benchmarking and learning about error correction, it’s probably not the end of the story for fault-tolerant quantum computers.
Exploring “good” codes
The field of error correction buzzed with excitement in 2022 when Pavel Panteleev and Gleb Kalachev at Moscow State University published a landmark paper proving that there exist asymptotically good codes — codes where the number of extra qubits needed levels off as the quality of the code increases.
This has spurred a lot of new work in error correction, especially in the same family of codes that the surface code hails from, called quantum low-density parity check, or qLDPC codes. These qLDPC codes are quantum error correcting codes where the operations responsible for checking whether or not an error has occurred only have to act on a few qubits, and each qubit only has to participate in a few checks.
But this work was highly theoretical, focused on proving the possibility of this kind of error correction. It didn’t take into account the real constraints of building quantum computers. Most importantly, some qLDPC codes would require many qubits in a system to be physically linked to high numbers of other qubits. In practice, that would require quantum processors folded in on themselves in psychedelic hyper-dimensional origami, or entombed in wildly complex rats’ nests of wires.
In our paper, we looked for fault-tolerant quantum memory with a low qubit overhead, high error threshold, and a large code distance.
In our Nature paper, we specifically looked for fault-tolerant quantum memory with a low qubit overhead, high error threshold, and a large code distance.
Let’s break that down:
-
Fault-tolerant: The circuits used to detect errors won't spread those errors around too badly in the process, and they can be corrected faster than they occur
-
Quantum memory: In this paper, we are only encoding and storing quantum information. We are not yet doing calculations on the encoded quantum information.
-
High error threshold: The higher the threshold, the higher amount of hardware errors the code will allow while still being fault tolerant. We were looking for a code that allowed us to operate the memory reliably at physical error rates as high as 0.001, so we wanted a threshold close to 1 percent.
-
Large code distance: Distance is the measure of how robust the code is — how many errors it takes to completely flip the value from 0 to 1 and vice versa. In the case of 00000 and 11111, the distance is 5. We wanted one with a large code distance that corrects more than just a couple errors. Large-distance codes can suppress noise by orders of magnitude even if the hardware quality is only marginally better than the code threshold. In contrast, codes with a small distance become useful only if the hardware quality is significantly better than the code threshold.
-
Low qubit overhead: Overhead is the number of extra qubits required for correcting errors. We want the number of qubits required to do error correction to be far less than we need for a surface code of the same quality, or distance.
We’re excited to report that our team’s mathematical analysis found concrete examples of qLDPC codes that met all of these required conditions. These fall into a family of codes called “Bivariate Bicycle (BB)” codes. And they are going to shape not only our research going forward, but how we architect physical quantum systems.
The gross code
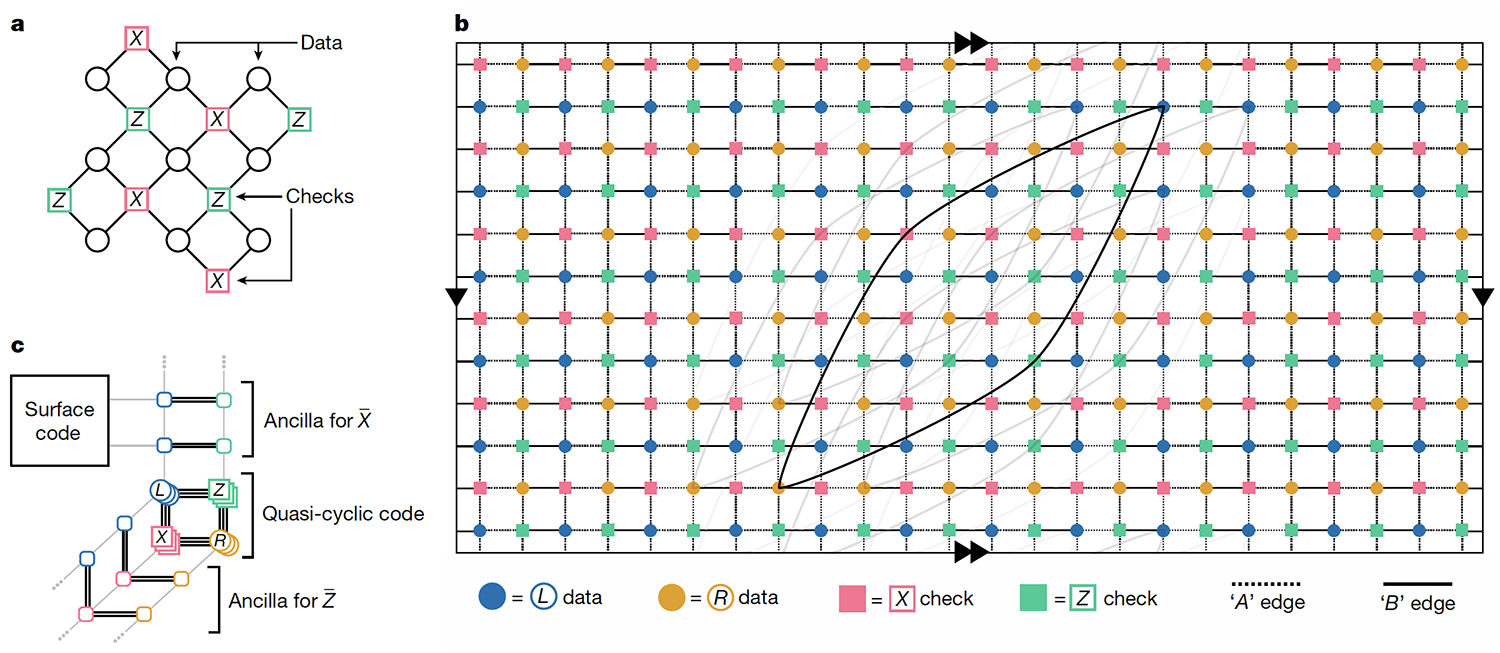
While many qLDPC code families show great promise for advancing error correction theory, most aren’t necessarily pragmatic for real-world application. Our new codes lend themselves better to practical implementation because each qubit needs only to connect to six others, and the connections can be routed on just two layers.
To get an idea of how the qubits are connected, imagine they are put onto a square grid, like a piece of graph paper. Curl up this piece of graph paper so that it forms a tube, and connect the ends of the tube to make a donut. On this donut, each qubit is connected to its four neighbors and two qubits that are farther away on the surface of the donut. No more connections needed.
The good news is we don’t actually have to embed our qubits onto a donut to make these codes work — we can accomplish this by folding the surface differently and adding a few other long-range connectors to satisfy mathematical requirements of the code. It’s an engineering challenge, but much more feasible than a hyper-dimensional shape.
We explored some codes that have this architecture and focused on a particular [[144,12,12]] code. We call this code the gross code because 144 is a gross (or a dozen dozen). It requires 144 qubits to store data — but in our specific implementation, it also uses another 144 qubits to check for errors, so this instance of the code uses 288 qubits. It stores 12 logical qubits well enough that fewer than 12 errors can be detected. Thus: [[144,12,12]].
Using the gross code, you can protect 12 logical qubits for roughly a million cycles of error checks using 288 qubits. Doing roughly the same task with the surface code would require nearly 3,000 qubits.
This is a milestone. We are still looking for qLDPC codes with even more efficient architectures, and our research on performing error-corrected calculations using these codes is ongoing. But with this publication, the future of error correction looks bright.
Fig. 1 | Tanner graphs of surface and BB codes.
Fig. 1 | Tanner graphs of surface and BB codes. a, Tanner graph of a surface code, for comparison. b, Tanner graph of a BB code with parameters [[144, 12, 12]] embedded into a torus. Any edge of the Tanner graph connects a data and a check vertex. Data qubits associated with the registers q(L) and q(R) are shown by blue and orange circles. Each vertex has six incident edges including four short-range edges (pointing north, south, east and west) and two long-range edges. We only show a few long-range edges to avoid clutter. Dashed and solid edges indicate two planar subgraphs spanning the Tanner graph, see the Methods. c, Sketch of a Tanner graph extension for measuring and following ref. 50, attaching to a surface code. The ancilla corresponding to the measurement can be connected to a surface code, enabling load-store operations for all logical qubits by means of quantum teleportation and some logical unitaries. This extended Tanner graph also has an implementation in a thickness-2 architecture through the A and B edges (Methods).
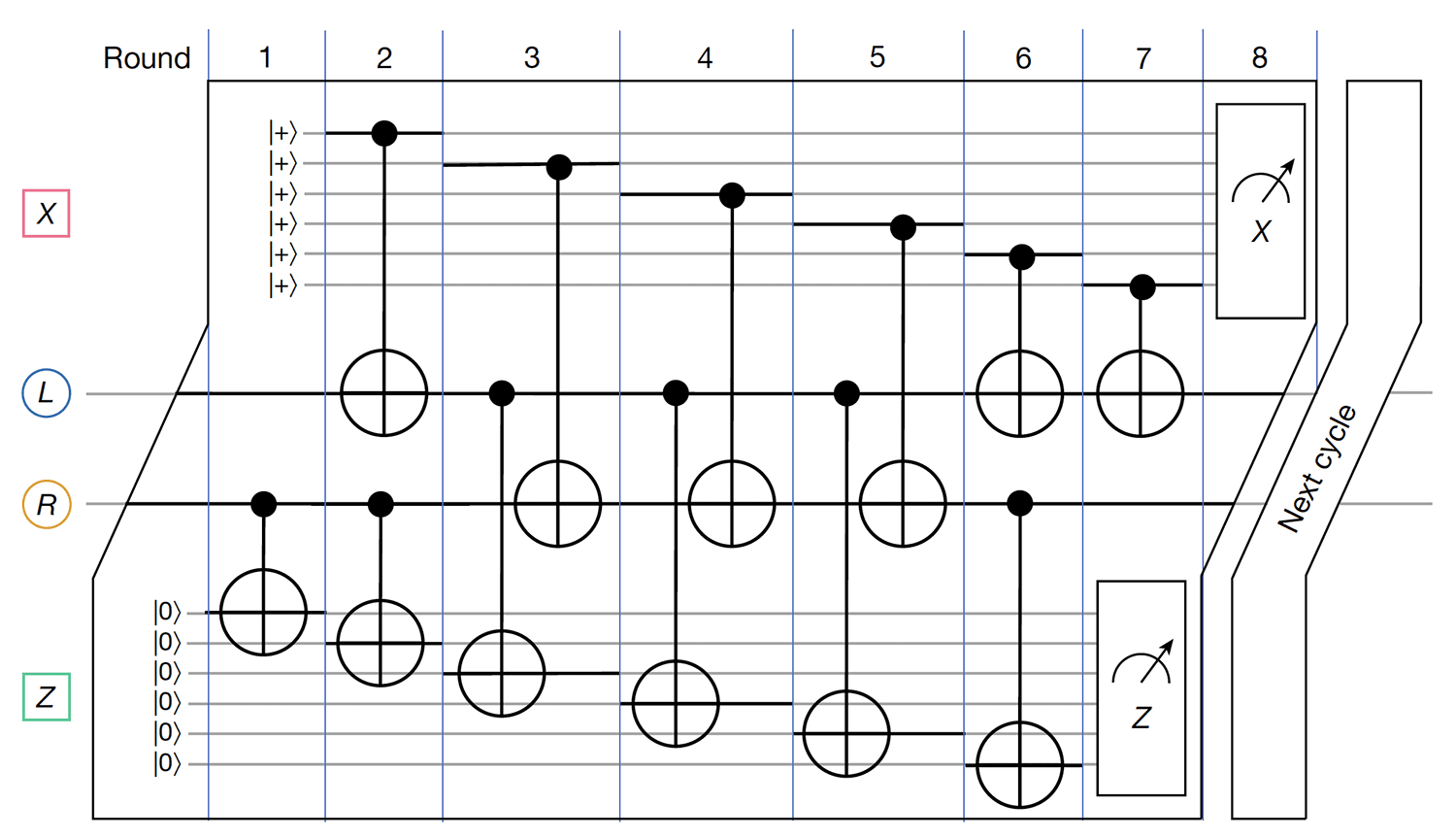
Fig. 2 | Syndrome measurement circuit.
Fig. 2 | Syndrome measurement circuit. Full cycle of syndrome measurements relying on seven layers of CNOTs. We provide a local view of the circuit that only includes one data qubit from each register q(L) and q(R). The circuit is symmetric under horizontal and vertical shifts of the Tanner graph. Each data qubit is coupled by CNOTs with three X-check and three Z-check qubits: see the Methods for more details.
Why error correction matters
This code is part of our broader strategy to bring useful quantum computing to the world.
Today, our users benefit from novel error mitigation techniques — methods for reducing or eliminating the effect of noise when calculating observables, alongside our work suppressing errors at the hardware level. This work brought us into the era of quantum utility. IBM researchers and partners all over the world are exploring practical applications of quantum computing today with existing quantum systems. Error mitigation lets users begin looking for quantum advantage on real quantum hardware.
But error mitigation comes with its own overhead, requiring running the same executions repeatedly so that classical computers can use statistical methods to extract an accurate result. This limits the scale of the programs you can run, and increasing that scale requires tools beyond error mitigation — like error correction.
Last year, we debuted a new roadmap laying out our plan to continuously improve quantum computers over the next decade. This new paper is an important example of how we plan to continuously increasing the complexity (number of gates) of the quantum circuits that can be run on our hardware. It will allow us to transition from running circuits with 15,000 gates to 100 million, or even 1 billion gates.






















 More than ever, there is a demand for IT to deliver innovation. Your IBM i has been an essential part of your business operations for years. However, your organization may struggle to maintain the current system and implement new projects. The thousands of customers we've worked with and surveyed state that expectations regarding the digital footprint and vision of the company are not aligned with the current IT environment.
More than ever, there is a demand for IT to deliver innovation. Your IBM i has been an essential part of your business operations for years. However, your organization may struggle to maintain the current system and implement new projects. The thousands of customers we've worked with and surveyed state that expectations regarding the digital footprint and vision of the company are not aligned with the current IT environment. TRY the one package that solves all your document design and printing challenges on all your platforms. Produce bar code labels, electronic forms, ad hoc reports, and RFID tags – without programming! MarkMagic is the only document design and print solution that combines report writing, WYSIWYG label and forms design, and conditional printing in one integrated product. Make sure your data survives when catastrophe hits. Request your trial now! Request Now.
TRY the one package that solves all your document design and printing challenges on all your platforms. Produce bar code labels, electronic forms, ad hoc reports, and RFID tags – without programming! MarkMagic is the only document design and print solution that combines report writing, WYSIWYG label and forms design, and conditional printing in one integrated product. Make sure your data survives when catastrophe hits. Request your trial now! Request Now. Forms of ransomware has been around for over 30 years, and with more and more organizations suffering attacks each year, it continues to endure. What has made ransomware such a durable threat and what is the best way to combat it? In order to prevent ransomware, organizations must first understand how it works.
Forms of ransomware has been around for over 30 years, and with more and more organizations suffering attacks each year, it continues to endure. What has made ransomware such a durable threat and what is the best way to combat it? In order to prevent ransomware, organizations must first understand how it works. Disaster protection is vital to every business. Yet, it often consists of patched together procedures that are prone to error. From automatic backups to data encryption to media management, Robot automates the routine (yet often complex) tasks of iSeries backup and recovery, saving you time and money and making the process safer and more reliable. Automate your backups with the Robot Backup and Recovery Solution. Key features include:
Disaster protection is vital to every business. Yet, it often consists of patched together procedures that are prone to error. From automatic backups to data encryption to media management, Robot automates the routine (yet often complex) tasks of iSeries backup and recovery, saving you time and money and making the process safer and more reliable. Automate your backups with the Robot Backup and Recovery Solution. Key features include: Business users want new applications now. Market and regulatory pressures require faster application updates and delivery into production. Your IBM i developers may be approaching retirement, and you see no sure way to fill their positions with experienced developers. In addition, you may be caught between maintaining your existing applications and the uncertainty of moving to something new.
Business users want new applications now. Market and regulatory pressures require faster application updates and delivery into production. Your IBM i developers may be approaching retirement, and you see no sure way to fill their positions with experienced developers. In addition, you may be caught between maintaining your existing applications and the uncertainty of moving to something new. IT managers hoping to find new IBM i talent are discovering that the pool of experienced RPG programmers and operators or administrators with intimate knowledge of the operating system and the applications that run on it is small. This begs the question: How will you manage the platform that supports such a big part of your business? This guide offers strategies and software suggestions to help you plan IT staffing and resources and smooth the transition after your AS/400 talent retires. Read on to learn:
IT managers hoping to find new IBM i talent are discovering that the pool of experienced RPG programmers and operators or administrators with intimate knowledge of the operating system and the applications that run on it is small. This begs the question: How will you manage the platform that supports such a big part of your business? This guide offers strategies and software suggestions to help you plan IT staffing and resources and smooth the transition after your AS/400 talent retires. Read on to learn:
LATEST COMMENTS
MC Press Online